What is the difference in Broadband technologies?
According to the Federal Communications Commission (FCC), Broadband or high-speed Internet access allows users to access the Internet and Internet-related services at significantly higher speeds than those available through "dial-up" services. Broadband speeds vary significantly depending on the technology and level of service ordered. Broadband services for residential consumers typically provide faster downstream speeds (from the Internet to your computer) than upstream speeds (from your computer to the Internet).
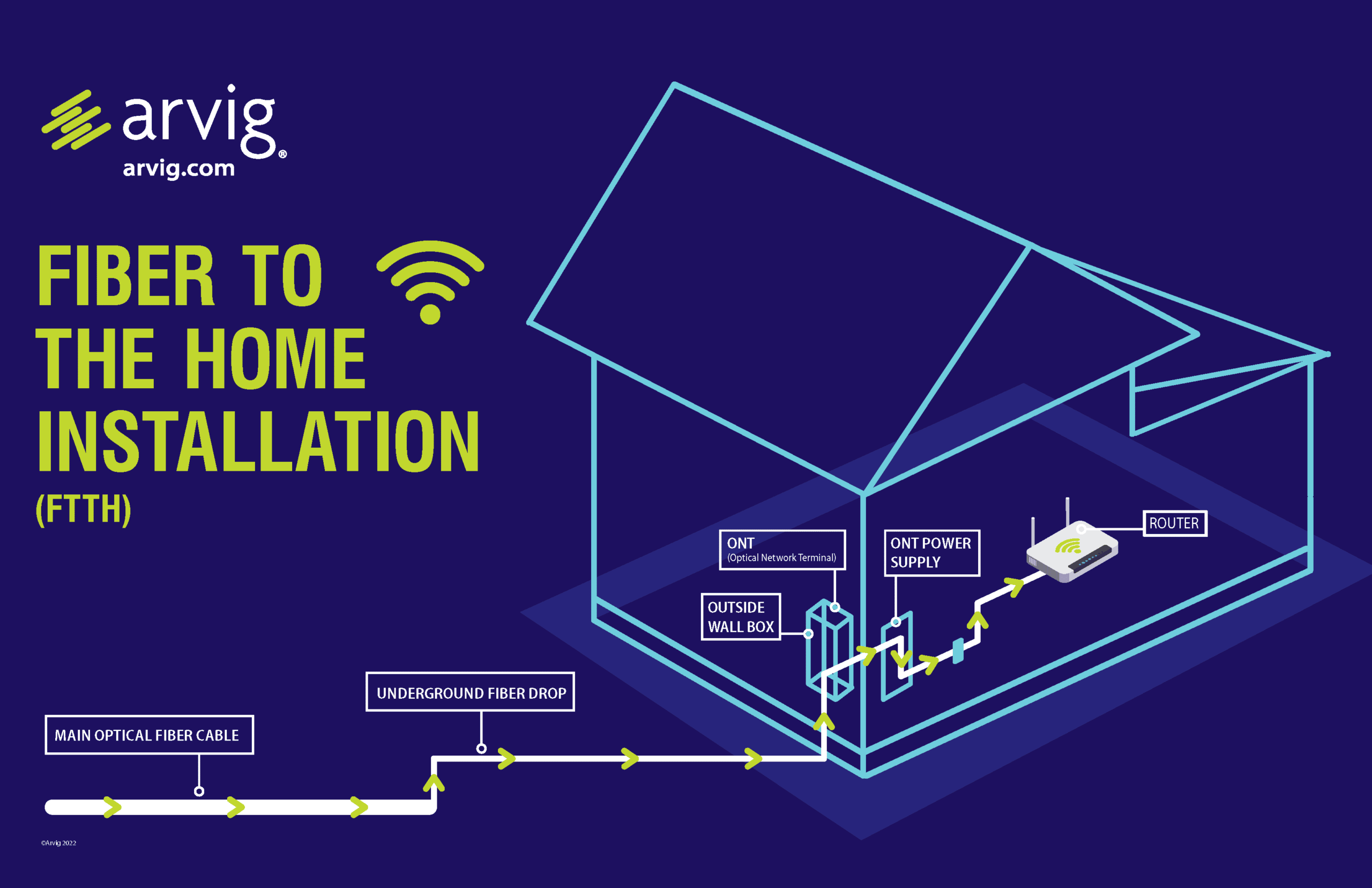
Fiber Optic
FIBER-OPTIC internet is a technology that allows the transmission of information in the form of light rather than electricity. There are many pieces that make up this advanced technology, but two key components are optical fibers and the so-called “last mile” of the fiber-optic network. Optical fibers are small, about 125 microns in diameter, or slightly larger than a human hair. Many of these fibers are bundled together to form cables (not to be confused with coaxial cables, which are made of copper). Light is transmitted down the fiber in LED or Laser pulses that travel extremely fast. These pulses carry binary data, which is a coding system that makes up everything seen on the Internet, even the words you are reading right now. Binary code is made up of bits, which are just ones and zeroes. These bits send messages in organized eight-part patterns, called bytes. It is easy to translate the bits of binary into light pulses. One pulse means one and no pulse means zero. These pulses can travel sixty miles before they experience any degradation. To transport data across thousands of miles these pulses go through optical amplifiers that boost their signal so that no data is lost.
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line/Loop)
DSL stands for Digital Subscriber Line/Loop and it is a communication medium that receives data via a copper telephone landline. DSL is the uses existing telephone wiring to transmit data via a DSL modem. A DSL modem receives signals via telephone lines and converts them digitally for the user. This data can be transferred wirelessly or via an ethernet cable. Phone lines have a higher capacity than required by phone calls, so DSL signals can easily piggyback across the same infrastructure.
Cable
CABLE internet service uses the same coaxial cable network as cable television to provide a home with internet. The internet service provider sends a data signal through the coaxial cable, or coax cable, into a home—specifically, to a modem. The modem then uses an ethernet cable to connect to a computer or router, which is what gives the user access to internet.
Fixed Wireless
FIXED WIRELESS internet service is delivered using transmitters to send and receive wireless internet signals directly from one point to another. These transmitters are affixed to stationary (fixed) objects, such as a poles, buildings, or towers—at strategic locations, combining to create a wireless network. Fixed wireless internet transmitters require a clear line of sight from one transmitter to another in order to function. Ensuring that lines of sight remain clear can be problematic because an internet provider can’t always control what happens between one transmitter and another. A tree could grow taller, a tall building could be constructed, a pole could get knocked over by adverse weather, all of which could potentially disrupt a fixed wireless transmission.
Mobile
MOBILE internet is accessed utilizing a cellular telephone service provider. It is wireless access that can handoff to another radio tower while it is moving across the service area.
Satellite
SATELLITE is a wireless internet beamed down from satellites orbiting the Earth. It’s much different from land-based internet services like cable or DSL, which transmit data through wires.
Redwood County assumes no responsibility or liability for any errors or omissions in the content of this site. The information contained in this site is provided on an "as is" basis with no guarantees of completeness, accuracy, usefulness or timeliness.